ECMAScript 6 (ES6) also known as ECMAScript 2015. ES6 is a significant update to the javascript. ES6 includes the following new features:
- Promise
- Class
- Arrow Function
- Template Strings
- Rest, Spread Operator
- Generators
- Destructuring
- Modules
Promise
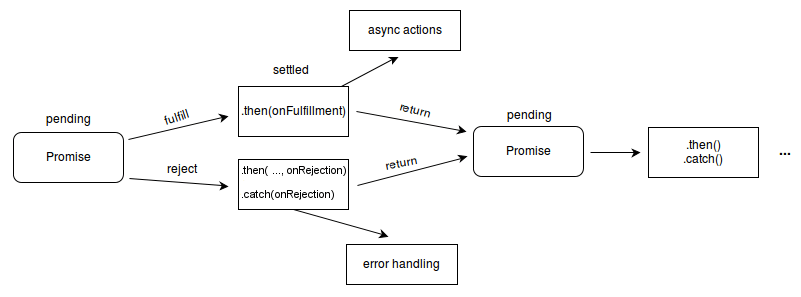
The Promise object represents the completion or failure of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value. A Promise has one of these states:
- pending: initial state, neither fulfilled nor rejected.
- fulfilled: meaning that the operation was completed successfully.
- rejected: meaning that the operation failed.
A promise is said to be settled if it's either fulfilled or rejected, but not pending.
Syntax-
const myPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { resolve("foo"); }); myPromise .then(handleFulfilledA, handleRejectedA) .then(handleFulfilledB, handleRejectedB);
Are you still using callback to handle asynchronous operations? If yes then it's time to replace callbacks with promises. Code become complex & not readable due to nested callbacks. Let's look at how we can migrate following callbacks to the promises.
Traditional callback hell
function getData(cb){ getApiData('/v1/api1',(apiData1)=>{ getApiData('/v1/api2',(apiData2)=>{ getApiData('/v1/api3',(apiData3)=>{ cb({ apiData1, apiData2, apiData3}); }); }); }); } getData(function successCb(data){ console.log(data); });
Using Promises
function getData(){ return Promise.all([ $getApiData('/v1/api1'), $getApiData('/v1/api2'), $getApiData('/v1/api3') ]) } getData().then(data=> console.log(data), err => console.log(err))
Methods & Must Read:
- Promise.all()
- Promise.allSettled()
- Promise.any()
- Promise.prototype.catch()
- Promise.prototype.finally()
- Promise.race()
- Promise.reject()
- Promise.resolve()
- Promise.prototype.then()